In This Article, We See Concepts Of JDK, JVM, JRE, JIT
JDK - Java Development Kit
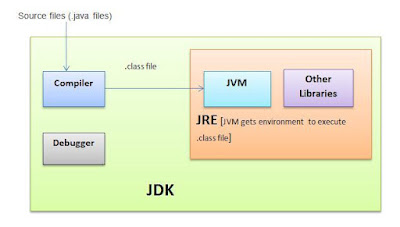
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment which is used to develop java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools.
JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle corporation:
- Standard Edition Java Platform
- Enterprise Edition Java Platform
- Micro Edition Java Platform
The JDK contains a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources such as an interpreter/loader (Java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (Javadoc) etc. to complete the development of a Java Application.
Components of JDK
Following is a list of primary components of JDK:
| appletviewer: | This tool is used to run and debug Java applets without a web browser. |
| apt: | It is an annotation-processing tool. |
| extcheck: | it is a utility that detects JAR file conflicts. |
| idlj: | An IDL-to-Java compiler. This utility generates Java bindings from a given Java IDL file. |
| jabswitch: | It is a Java Access Bridge. Exposes assistive technologies on Microsoft Windows systems. |
| java: | The loader for Java applications. This tool is an interpreter and can interpret the class files generated by the javac compiler. Now a single launcher is used for both development and deployment. The old deployment launcher, jre, no longer comes with Sun JDK, and instead it has been replaced by this new java loader. |
| javac: | It specifies the Java compiler, which converts source code into Java bytecode. |
| javadoc: | The documentation generator, which automatically generates documentation from source code comments |
| jar: | The specifies the archiver, which packages related class libraries into a single JAR file. This tool also helps manage JAR files. |
| javafxpackager: | It is a tool to package and sign JavaFX applications. |
| jarsigner: | the jar signing and verification tool. |
| javah: | the C header and stub generator, used to write native methods. |
| javap: | the class file disassembler. |
| javaws: | the Java Web Start launcher for JNLP applications. |
| JConsole: | Java Monitoring and Management Console. |
| jdb: | the debugger. |
| jhat: | Java Heap Analysis Tool (experimental). |
| jinfo: | This utility gets configuration information from a running Java process or crash dump. |
| jmap: | Oracle jmap - Memory Map- This utility outputs the memory map for Java and can print shared object memory maps or heap memory details of a given process or core dump. |
| jmc: | Java Mission Control |
| jps: | Java Virtual Machine Process Status Tool lists the instrumented HotSpot Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) on the target system. |
| jrunscript: | Java command-line script shell. |
| jstack: | It is a utility that prints Java stack traces of Java threads (experimental). |
| jstat: | Java Virtual Machine statistics monitoring tool (experimental). |
| jstatd: | jstat daemon (experimental). |
| keytool: | It is a tool for manipulating the keystore. |
| pack200: | JAR compression tool. |
| Policytool: | It specifies the policy creation and management tool, which can determine policy for a Java runtime, specifying which permissions are available for code from various sources. |
| VisualVM: | It is a visual tool integrating several command-line JDK tools and lightweight [clarification needed] performance and memory profiling capabilities |
| wsimport: | It generates portable JAX-WS artifacts for invoking a web service. |
| xjc: | It is the part of the Java API for XML Binding (JAXB) API. It accepts an XML schema and generates Java classes. |
JVM - Java Virtual Machine
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (i.e. JVM is platform dependent).
It is:
- A specification where working of Java Virtual Machine is specified. But implementation provider is independent to choose the algorithm. Its implementation has been provided by Oracle and other companies.
- An implementation Its implementation is known as JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
- Runtime Instance Whenever you write java command on the command prompt to run the java class, an instance of JVM is created.
What it does:
- The JVM performs following operation:
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
JVM provides definitions for the:
- Memory area
- Class file format
- Register set
- Garbage-collected heap
- Fatal error reporting etc.
JRE- Java Runtime Environment
Java Run-time Environment (JRE) is the part of the Java Development Kit (JDK). It is a freely available software distribution which has Java Class Library, specific tools, and a stand-alone JVM. It is the most common environment available on devices to run java programs. The source Java code gets compiled and converted to Java bytecode. If you wish to run this bytecode on any platform, you require JRE. The JRE loads classes, verify access to memory, and retrieves the system resources. JRE acts as a layer on the top of the operating system.
It also includes:
- Technologies which get used for deployment such as Java Web Start.
- Toolkits for user interface like Java 2D.
- Integration libraries like Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI).
- Libraries such as Lang and util.
- Other base libraries like Java Management Extensions (JMX), Java Native Interface (JNI) and Java for XML Processing (JAX-WS).
JIT - Just In Time (Compiler)
The JIT compilation includes two approaches AOT (Ahead-of-Time compilation) and interpretation to translate code into machine code. AOT compiler compiles the code into a native machine language (the same as the normal compiler). It transforms the bytecode of a VM into the machine code. The following optimizations are done by the JIT compilers:
- Method In-lining
- Local Optimizations
- Control Flow Optimizations
- Constant Folding
- Dead Code Elimination
- Global Optimizations
- Heuristics for optimizing call sites
Advantages of JIT Compiler
- It requires less memory usages.
- The code optimization is done at run time.
- It uses different levels of optimization.
- It reduces the page faults.
Disadvantages of JIT Compiler